An Action Potentional Can Best Be Described as
The nerve has to reach threshold voltage to initate conduction down the length of. Action potential an explosion of electrical activity thats created by a depolarizing current large brief reversal in polarity of an axon.
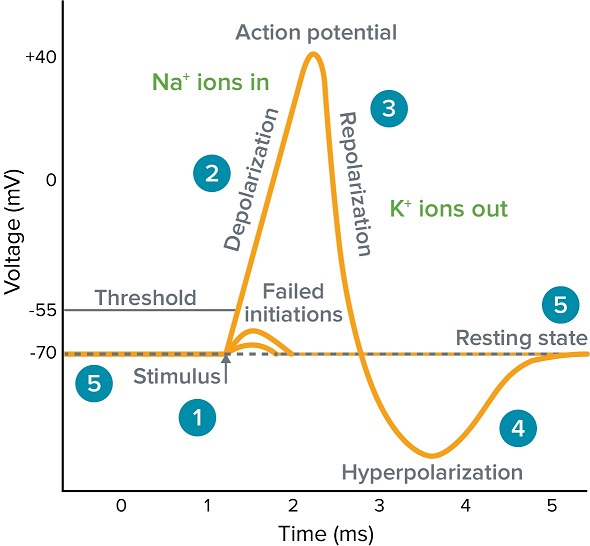
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart Membrane Potential Molecular Devices
Action potential is passively propogated down the axon.

. The information is sent via electro-chemical signals known as action potentials that travel down the length of the neuron. Action potential refers to a change in the electrical potential which is associated with the transmission of impulses along the membrane of a nerve cell or muscle cell. - This can be described as the Unidirectional propagation of the AP.
An action potential is a predictable change in membrane potential that occurs due to the open and closing of voltage gated ion channels on the cell membrane. When neurons transmit signals through the body part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential. View the full answer.
What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in. Action potential follow the all or none rules. Action potential Brief 1 ms electrical event typically generated in the axon that signals the neuron as active.
Thus in some situations a rise in the membrane potential can cause ion channels to open thereby causing a further rise in the. Cells of the sinoatrial node towards the membrane potential threshold. The nervous impulse is referred to as the action potential.
Dendrites and cell bodies tend to have ligand-gated ion channels. Then sodium and potassium permeability properties of the neuronal plasma membrane as well as their changes in response to alterations in the membrane potential are. The action potential and consequent transmitter release allow the neuron to communicate with other neurons.
It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs. What is an Action Potential.
Inside becomes positive relative to the outside. Saltatory propagation allows action potentials to spread _________ and ________ than ordinary action potentials along nerve cells that are not myelinated. At the peak action potential K channels open and K begins to leave the cell.
An action potential is a brief only a few milliseconds reversal of the membrane potential V m. An action potential is described as a sudden and spontaneous change or reversal in the membrane potential above a threshold value due to increased permeability of the cell membrane. Voltage-gated ion channels are capable of producing action potentials because they can give rise to positive feedback loops.
Cell need to come back to rest before another action potential can be fired - Are unidirectional. Action potential the brief about one-thousandth of a second reversal of electric polarization of the membrane of a nerve cell neuron or muscle cell. In the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement.
The pacemaker potential occurs at the end of one action potential and just before the start of the next. Action potential that jump along the nodes of Ranvier on nerves is known as. The membrane potential controls the state of the ion channels but the state of the ion channels controls the membrane potential.
This sequence is called the excitationcontractionrelaxation cycle. There have to be ion channels along the axon Rate of action potential depend upon capacitance axon diameter and density of ion channel. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication.
The process is initiated by a threshold level stimulus such as a nearby change in membrane potential threshold potential local. An action potential travels the length of the axon and causes release of neurotransmitter into the synapse. It is the slow depolarisation of the pacemaker cells eg.
- Have refractory periods ie. Where do action potentials take place. If the threshold of excitation is reached all Na channels open and the membrane depolarizes.
At rest the V m of a neuron is around 70 mV closer to the equilibrium potential for potassium V K but during an action potential V m transiently approaches 50 mV closer to the. Electrically Active Cell Membranes. These neurons are then triggered to release chemical messengers called neurotransmitters which help trigger action potentials in nearby cells and.
An early step in this cycle is the release of stored calcium from an intracellular membrane complex called the sarcoplasmic reticulum SR. This lecture describes the details of the neuronal action potential. An action potential AP is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Generation when stimulated nerve conducts impulse along its length. The lecture starts by describing the electrical properties of non-excitable cells as well as excitable cells such as neurons.
It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. The basis of this process is the action potential. The three main stages of an action potential are the depolarization repolarization and refractory period.
This process which occurs during the firing of the neurons allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon a portion of the neuron that. A stimulus from a sensory cell or another neuron causes the target cell to depolarize toward the threshold potential. A neuron a nerve cell is the basic building block of the nervous system.
It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. The action potential is generated at the ____ and conducted along the _____ axon hillock. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 7.
An action potential occurs when a portion of the membrane rapidly depolarizes and then repolarizes again to the original resting state. Alterations in voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels as well as in voltage-gated calcium and chloride channels are now known to be the basis of several diseases of nerve and muscle. The change in the membrane voltage from 70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change.
The muscle action potential triggers a sequence of actions that ultimately results in the contraction and relaxation of the muscle fiber. Permeability of the membrane translates to the action of the ion channels in allowing certain ions to enter the cell which would otherwise not be possible in the normal resting stage.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)
Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub

Laurasieltspage On Instagram In Academic Writing It S Really Important To Show The Difference Between Your Opinion And Facts Academic Writing Writing Facts

Neuron Action Potentials The Creation Of A Brain Signal Article Khan Academy

Pin By Jack Mankin On Biology Plasma Membrane Membrane Plasma
Comments
Post a Comment